Chapter 1: Real Numbers
Q.1. Find a rational number between √2 and √3.
Q.2. Prove that √2 is an irrational number.
Q.3. Prove that 2 + 5 √3 is an irrational number, given that √3 is an irrational number.
Q.4. The HCF of two numbers a and b is 5 and their LCM is 200. Find the product
Q.5. A number N when divided by 14 gives the remainder 5. What is the remainder when the same number is divided by 7?
Q.6. Express 429 as product of its prime factor ?
Q.7. Find the HCF of 612 and 1314 using prime factorisation.
Q.8. Write a rational number between √2 and √3 ?
Q.9. If HCF of 65 and 117 is expressible in the form 65n – 117, find the value of n ?
Q.10. prove that root 5 is irrational?
Chapter 2: Polynomials
Based on zeroes and coefficient
Question 1.
If the sum of zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 3x2 – kx + 6 is 3, then find the value of k. (2012)
Solution:
Here a = 3, b = -k, c = 6
Sum of the zeroes, (α + β) = −ba = 3 …..(given)
⇒ −(−k)3 = 3
⇒ k = 9
Question 2.
If α and β are the zeroes of the polynomial ax2 + bx + c, find the value of α2 + β2. (2013)
Solution: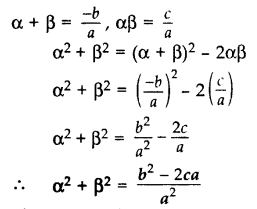
Question 3.
If the sum of the zeroes of the polynomial p(x) = (k2 – 14) x2 – 2x – 12 is 1, then find the value of k. (2017 D)
Solution:
p(x) = (k2 – 14) x2 – 2x – 12
Here a = k2 – 14, b = -2, c = -12
Sum of the zeroes, (α + β) = 1 …[Given]
⇒ −ba = 1
⇒ −(−2)k2−14 = 1
⇒ k2 – 14 = 2
⇒ k2 = 16
⇒ k = ±4
Question 4.
If α and β are the zeroes of a polynomial such that α + β = -6 and αβ = 5, then find the polynomial. (2016 D)
Solution:
Quadratic polynomial is x2 – Sx + P = 0
⇒ x2 – (-6)x + 5 = 0
⇒ x2 + 6x + 5 = 0
Question 5.
A quadratic polynomial, whose zeroes are -4 and -5, is …. (2016 D)
Solution:
x2 + 9x + 20 is the required polynomial.
Polynomials Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-I (2 Marks)
Question 6.
Find the condition that zeroes of polynomial p(x) = ax2 + bx + c are reciprocal of each other. (2017 OD)
Solution:
Let α and 1α be the zeroes of P(x).
P(a) = ax2 + bx + c …(given)
Product of zeroes = ca
⇒ α × 1α = ca
⇒ 1 = ca
⇒ a = c (Required condition)
Coefficient of x2 = Constant term
Question 7.
Form a quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are 3 + √2 and 3 – √2. (2012)
Solution:
Sum of zeroes,
S = (3 + √2) + (3 – √2) = 6
Product of zeroes,
P = (3 + √2) x (3 – √2) = (3)2 – (√2)2 = 9 – 2 = 7
Quadratic polynomial = x2 – Sx + P = x2 – 6x + 7
Question 8.
Find a quadratic polynomial, the stun and product of whose zeroes are √3 and 1√3 respectively. (2014)
Solution:
Sum of zeroes, (S) = √3
Product of zeroes, (P) = 1√3
Quadratic polynomial = x2 – Sx + P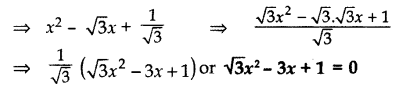
Question 9.
Find a quadratic polynomial, the sum and product of whose zeroes are 0 and -√2 respectively. (2015)
Solution:
Quadratic polynomial is
x2 – (Sum of zeroes) x + (Product of zeroes)
= x2 – (0)x + (-√2)
= x2 – √2
Question 10.
Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial √3 x2 – 8x + 4√3. (2013)
Solution: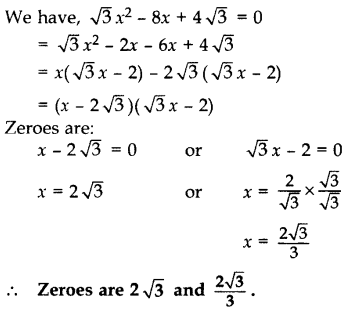
Question 11.
If the zeroes of the polynomial x2 + px + q are double in value to the zeroes of 2x2 – 5x – 3, find the value of p and q. (2012)
Solution:
We have, 2x2 – 5x – 3 = 0
= 2x2 – 6x + x – 3
= 2x(x – 3) + 1(x – 3)
= (x – 3) (2x + 1)
Zeroes are:
x – 3 = 0 or 2x + 1 = 0
⇒ x = 3 or x = −12
Since the zeroes of required polynomial is double of given polynomial.
Zeroes of the required polynomial are:
3 × 2, (−12 × 2), i.e., 6, -1
Sum of zeroes, S = 6 + (-1) = 5
Product of zeroes, P = 6 × (-1) = -6
Quadratic polynomial is x2 – Sx + P
⇒ x2 – 5x – 6 …(i)
Comparing (i) with x2 + px + q
p = -5, q = -6
Question 12.
Can (x – 2) be the remainder on division of a polynomial p(x) by (2x + 3)? Justify your answer. (2016 OD)
Solution:
In case of division of a polynomial by another polynomial, the degree of the remainder (polynomial) is always less than that of the divisor. (x – 2) can not be the remainder when p(x) is divided by (2x + 3) as the degree is the same.
Question 13.
Find a quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are 3+√55 and 3−√55. (2013)
Solution: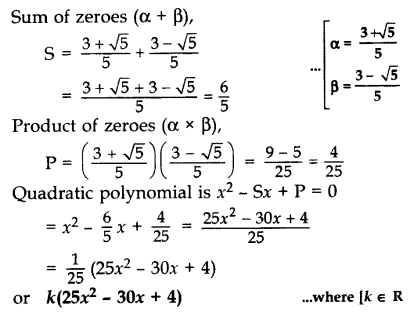
Question 14.
Find the quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are -2 and -5. Verify the relationship between zeroes and coefficients of the polynomial. (2013)
Solution:
Sum of zeroes, S = (-2) + (-5) = -7
Product of zeroes, P = (-2)(-5) = 10
Quadratic polynomial is x2 – Sx + P = 0
= x2 – (-7)x + 10
= x2 + 7x + 10
Verification:
Here a = 1, b = 7, c = 10
Sum of zeroes = (-2) + (-5) = 7
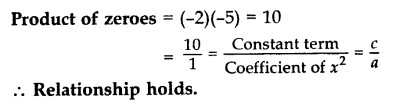
Question 15.
Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 3x2 – 75 and verify the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients. (2014)
Solution:
We have, 3x2 – 75
= 3(x2 – 25)
= 3(x2 – 52)
= 3(x – 5)(x + 5)
Zeroes are:
x – 5 = 0 or x + 5 = 0
x = 5 or x = -5
Verification:
Here a = 3, b = 0, c = -75
Sum of the zeroes = 5 + (-5) = 0
Question 16.
Find the zeroes of p(x) = 2x2 – x – 6 and verify the relationship of zeroes with these co-efficients. (2017 OD)
Solution:
p(x) = 2x2 – x – 6 …[Given]
= 2x2 – 4x + 3x – 6
= 2x (x – 2) + 3 (x – 2)
= (x – 2) (2x + 3)
Zeroes are:
x – 2 = 0 or 2x + 3 = 0
x = 2 or x = −32
Verification:
Here a = 2, b = -1, c = -6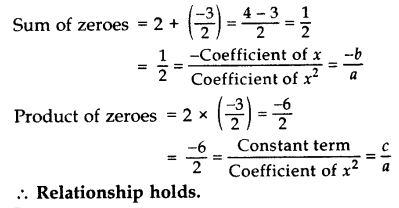
Question 17.
What must be subtracted from the polynomial f(x) = x4 + 2x3 – 13x2 – 12x + 21 so that the resulting polynomial is exactly divisible by x2 – 4x + 3? (2012, 2017 D)
Solution: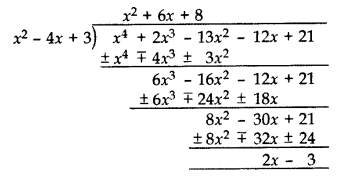
(2x – 3) should be subtracted from x4 + 2x3 – 13x2 – 12x + 21.
Polynomials Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-II (3 Marks)
Question 18.
Verify whether 2, 3 and 12 are the zeroes of the polynomial p(x) = 2x3 – 11x2 + 17x – 6. (2012, 2017 D)
Solution:
p(x) = 2x3 – 11x2 + 17x – 6
When x = 2,
p(2) = 2(2)3 – 11(2)2 + 17(2) – 6 = 16 – 44 + 34 – 6 = 0
When x = 3, p(3) = 2(3)3 – 11(3)2 + 17(3) – 6 = 54 – 99 + 51 – 6 = 0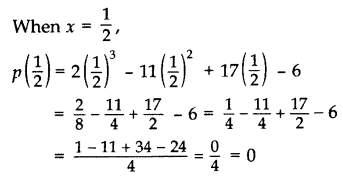
Yes, x = 2, 3 and 12 all are the zeroes of the given polynomial.
Class 10 guides
Question 19.
Show that 12 and −32 are the zeroes of the polynomial 4x2 + 4x – 3 and verify the relationship between zeroes and co-efficients of polynomial. (2013)
Solution:
Let P(x) = 4x2 + 4x – 3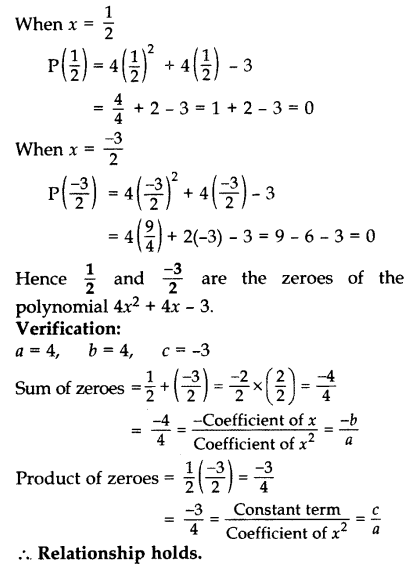
Question 20.
Find a quadratic polynomial, the sum and product of whose zeroes are -8 and 12 respectively. Hence find the zeroes. (2014)
Solution:
Let Sum of zeroes (α + β) = S = -8 …[Given]
Product of zeroes (αβ) = P = 12 …[Given]
Quadratic polynomial is x2 – Sx + P
= x2 – (-8)x + 12
= x2 + 8x + 12
= x2 + 6x + 2x + 12
= x(x + 6) + 2(x + 6)
= (x + 2)(x + 6)
Zeroes are:
x + 2 = 0 or x + 6 = 0
x = -2 or x = -6
Chapter 3: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Word problems: These include age problems (e.g., finding present ages given past and future relationships) and problems involving speed, distance, and time (e.g., calculating the speed of a stream given upstream and downstream travel times). Solving systems of equations using appropriate methods is also a common question type.
Graphical and algebraic solutions: Questions involve interpreting graphs of linear equations to find triangle vertices and determining conditions for infinitely many solutions in a pair of linear equations.
Chapter 4: Quadratic Equations
Nature of roots: Key questions involve finding the nature of roots using the discriminant, determining the value of a variable for equal roots, and proving when an equation has no real roots.
Word problems: These include problems related to train travel with varying speeds and time, and calculating the sides of squares given the sum of their areas and the difference of their perimeters.
Chapter 5: Arithmetic Progressions
Basic applications of formulas: This section focuses on finding specific terms of an AP and calculating the number of terms needed for a given sum. Problems may also involve finding the first term, sum of initial terms, and the n-th term when the sum of the first n terms is given.
Advanced word problems: Questions can involve finding the ratio of the 9th terms of two APs given the ratio of the sum of their first n terms, or finding consecutive numbers in an AP based on their sum and the ratio of products of terms.
Chapter 6: Triangles
Based on similarity: Important questions include using similarity to prove proportional sides in a trapezium, finding the area of a larger similar triangle given the ratio of sides and the area of the smaller triangle, and proving relationships in similar right triangles.
Pythagoras theorem: Applications of the theorem, such as calculating the height a ladder reaches on a wall, are also important.
Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry
Distance formula: Questions involve finding points on an axis equidistant from two given points and using the distance formula to verify geometric properties like whether given points form a square. Determining if points are collinear is also a common problem.
Section formula: Key questions include finding the coordinates of points that divide a line segment into equal parts and determining the ratio in which a point divides a line segment.
Chapter 8: Introduction to Trigonometry
Basic relations: This involves finding trigonometric ratios in a right-angled triangle given side lengths and calculating other ratios when one is given.
Trigonometric identities: Important questions require proving trigonometric identities and simplifying expressions.
Conditional relations: Questions may involve finding angles when given trigonometric values of sums and differences of those angles.
Chapter 9: Some Applications of Trigonometry
Single triangle problems: These include calculating the height of a tower given the angle of elevation and distance from the base, and finding the length of a ladder given its angle with the horizontal and distance from the wall.
Combined angle problems: Important questions involve using angles of elevation and depression to find distances and heights between a ship and a hill, or finding the height of a tower and distance from a building using angles of depression from the tower’s top.
Chapter 10: Circles
Tangent properties: Key questions include using the tangent-radius theorem to find the radius of a circle, proving that tangents from an external point are equal in length, and proving that tangents at the ends of a diameter are parallel.
Combined figures: Problems may involve proving properties of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle.
Chapter 11: Areas Related to Circles
Perimeter and area calculations: Important questions involve finding the area of minor and major segments of a circle and calculating the area of a sector given its perimeter and radius.
Composite figures: Problems include calculating the number of revolutions of a car wheel and finding the area of a design formed within a circular table cover.
Chapter 12: Surface Areas and Volumes
Combined solids: This includes problems where a cone is placed in a cylinder filled with water to find the remaining water volume, calculating the volume of wood in a pen stand with conical and cubical depressions, and finding the volume of a frustum of a cone.
Chapter 13: Statistics
Measures of central tendency: Important questions involve calculating mean, median, and mode for grouped data, and finding missing frequencies when a measure of central tendency is given.
Cumulative frequency curves: Questions may require drawing ogives to find the median graphically.
Chapter 14: Probability
Simple probability: This includes problems involving cards, dice, and coins, as well as scenarios with bags of colored balls.
Conditional events: Important questions involve finding the probability of events connected by ‘or’ and ‘and’, and calculating the probability of non-defective items.


